Forget ABC: Data Backup Is as Easy as 3-2-1

In today’s world, technology dominates, with artificial intelligence enabling breakthroughs at a faster rate than ever. This rush has created an explosion of data, from customer data to product code, intellectual property, multimedia content and more.
With data increasingly essential to any business, data loss has the potential to be catastrophic and there are plenty of ways it can happen. That ranges from accidental deletion to hardware failure, a cyber attack and even natural disasters. A comprehensive data back-up strategy is no longer a nice to have, it is essential.
In the event of a data loss event you could lose:
- Your code
- Your customer data
- Your internal operations details
- Your financial performance records
- Your marketing insights
There’s no way your business can function without them.
That’s why data backups act as a safety net. They ensure that if the worst happens, you can quickly restore your operations with minimal disruption. Not only that, but they are essential for compliance in industries which are bound by data retention laws, including finance, healthcare, and legal services.
But the good news is that developing a robust data backup process has never been easier, or more affordable.
Data Backup Strategies: What Works

An effective backup strategy isn’t just about copying files, the process is about consistency, redundancy, and recovery.
You can think of it as a fire drill in your office, just more regular and less disruptive. Like a fire drill, there are a number of strategies that are proven, battle-hardened and ideal for your business.
That starts with the 3-2-1 rule, which is the gold standard in data back-up.
That’s our focus for this week. This is the first in a mini-series which will cover other strategies, including 3-2-1-1-0 and 4-3-2.
3-2-1 Rule
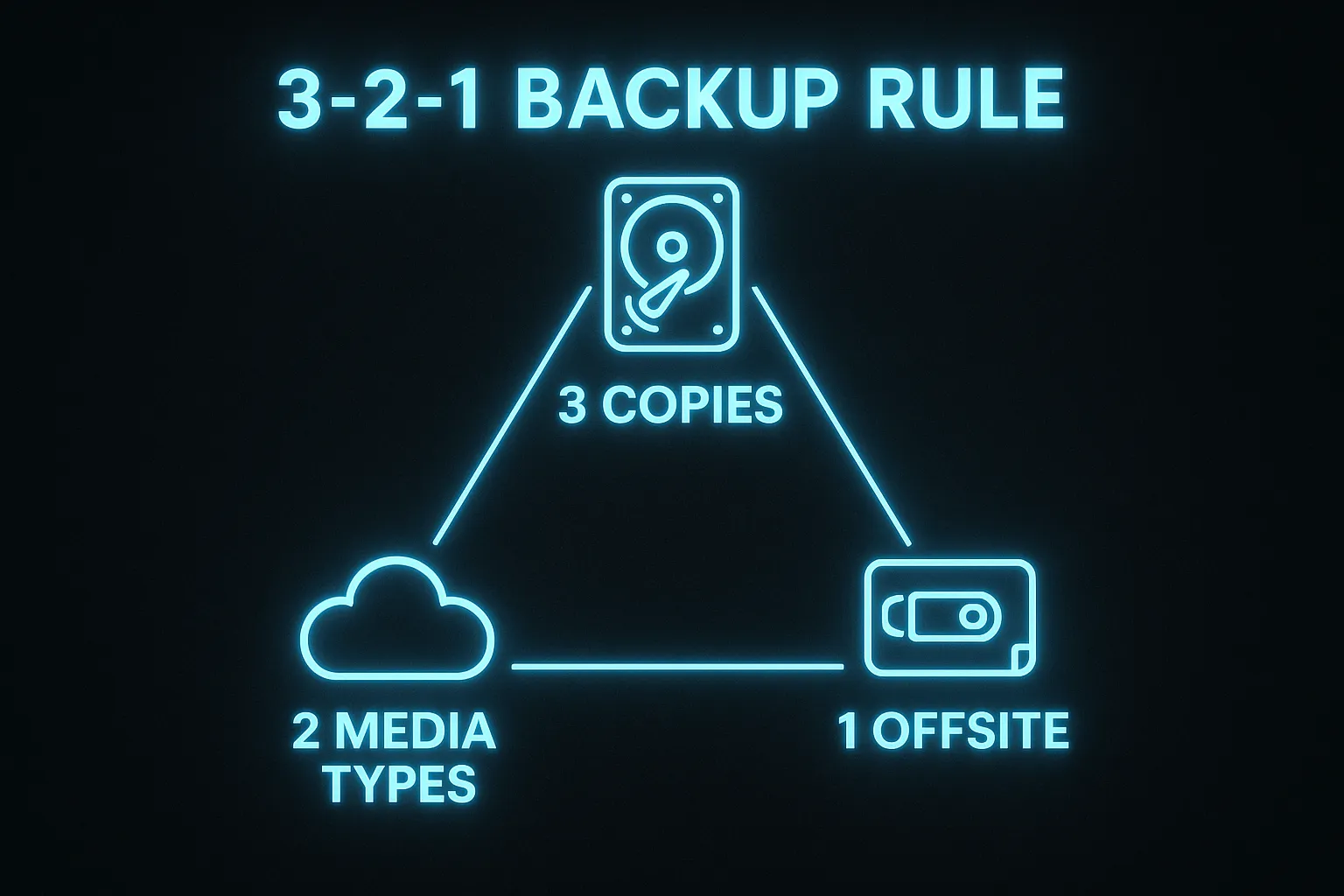
In a nutshell 3-2-1 works as follows:
- 3 copies of your data
- Stored on 2 different media types (such as local server and cloud)
- With 1 copy stored offsite or offline
This approach ensures redundancy. That means that if one copy fails or is compromised, the others remain intact. It uses both physical and cloud-based solutions to guard against hardware failures, while offsite backups protect against local disasters like fires or floods.
While 3-2-1 may be the best policy for effective and efficient data back-ups, there’s plenty more to explore and implement.
Further Best Practices
Versioning: Maintain multiple versions of your backups so you can roll back to a specific point in time. This is especially useful in cases of ransomware or file corruption.
Automated Scheduling: This lets your backups run at regular intervals. Manual backups can be forgotten or skipped, which can lead to outdated data.
Testing Recovery: Backups are only useful if they work. Running regular test recovery processes will ensure data can be restored quickly and completely.
Encryption: This may seem obvious but it’s worth stating: you should always encrypt backup data, especially when it is offsite or in the cloud, in order to protect against unauthorised access.
Weighing the Cost of Data Backups

It’s easy to look at data backups as being an additional cost that a company does not need to bear, especially if it is a young startup that’s cautiously managing its expenses. But the cost of not backing up data can be far greater, to the point that it could break your business altogether.
On the plus side, the cost of backup systems doesn’t have to be crazy. There are plenty of strategies and tools that can be used to build a robust process, without breaking the bank.
Some cost considerations may include:
Storage Costs: Cloud storage fees can add up, especially with large data sets. On-premise hardware also requires investment and maintenance.
Bandwidth: Backing up to the cloud consumes network resources. Businesses with limited bandwidth may need to schedule backups during off-peak hours.
Staffing: Managing backup systems requires time and expertise, particularly for manual or hybrid approaches.
Software Licenses: Backup platforms charge based on storage capacity, endpoints, or users. Beware of any products offering services for free.
Cloud providers and backup-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms are increasingly making data protection more accessible with scalable pricing models. That can be helpful for smaller companies but, ultimately, the cost must be weighed against the value of your data and the impact of potential data loss.
The Future of Data Backups

The backup landscape is evolving quickly, driven by AI, edge computing, and an increasingly remote workforce. We don’t have a crystal ball but here are some areas we are keeping a close eye on.
AI-Driven Backup Management
AI and machine learning are making backups smarter. Modern backup tools can now identify critical files, detect unusual activity (such as ransomware behaviour), and optimise storage allocation. And it’s all done automatically. This could reduce human error and ensure faster, more targeted recovery.
Immutable Backups
Immutable backups are a key line of defense against ransomware. These backups cannot be altered or deleted within a set period, even by admins. This is a core part of what we offer at SpaceTime, and we see vendors increasingly integrating this capability into their offerings as cyber threats grow more sophisticated.
You can read more about immutable backups here.
Cloud-Native Backups
As more businesses move to the cloud, traditional backup methods are being replaced by cloud-native solutions. These tools are designed to work with SaaS apps (like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce), providing backup and recovery tailored to modern workflows.
Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS)
BaaS solutions handle everything on behalf of businesses, from configuration to monitoring to recovery. These are especially valuable for small and medium-sized businesses that lack dedicated in-house IT resources. You can expect continued growth in this market as data complexity increases.
Conclusion: Data Backups Are a Business Imperative

Data backups are not just a box to check, they’re a business-critical function that protects your operations, customers, and reputation. In a landscape where threats are growing and data is only becoming more central to business success, a proactive, strategic approach to backup is essential.
Whether you’re building a plan from scratch or refining an existing strategy, stick to tried-and-tested frameworks like the 3-2-1 rule, automate your processes, and invest in solutions that scale with your needs.
The future of data backup is smarter, more secure, and more accessible than ever. It’s up to you to take the first step.



